Brief Introduction to Storage Area Network
Hmmm looks like you want to know and understand the so-called SAN(Storage Area Network). For a better understanding, I'm going to split each topic into section vice and without wasting any further time let's start the series with a brief introduction.
In the olden days, storage was available in the form of tape drives, Harddisk, CD, SSD and so on......
As time passes the demand for storage capacity, speed, performance, availability increased and parallelly there was a relevant advancement in the technology. Currently, NVMe is the most widely used technology for storage access.
Storage can be accessed in various ways and below are some of them
1. Local Access
- DAS - Direct Attached Storage
2. Remote Access
- SAN - Storage Area Network where the storage is accessed through storage protocol like SCSI, FCoE, FC, iSCSI, NVMe.
- NAS - Network-attached storage where the mode of access at the file level.
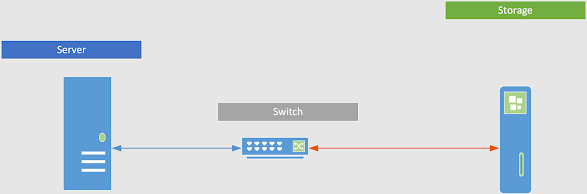
The main component involved in the SAN is server, san switches, and Storage. Some of the server vendors are Dell, DellEMC, HP, IBM. SAN Switch vendors are Brocade, Cisco ..etc. Storage vendors are Dell, NetApp, HP...
As shown in the above figure a host/server is connected to Storage through SAN switches. The communication happens by using any of the storage protocols like SCSI.
- RAID - Redundant Array of Independent Disks
- Data Replication



Comments
Post a Comment